|
Q: What is Cellular Digital Packet Data? |
A second method of transmitting data over cellular is a new technology called Cellular Digital Packet Data (CDPD). CDPD lets users send high-speed bursts of data, called "packets", over the existing cellular network, without interfering with normal voice conversations. CDPD is strategic to the cellular industry and to consumers because it optimizes cellular channels and provides a more cost effective method of sending small to medium amounts of data. Developed by IBM® and a consortium of major cellular providers, CDPD is a connectionless multi-protocol packet system that overlays the existing cellular AMPS network.
Connectionless means that each unit of data, referred to as a datagram, is routed and handled independently of all other datagrams on the network . CDPD routes each datagram throughout the cellular system based on the address information carried in the datagram header.
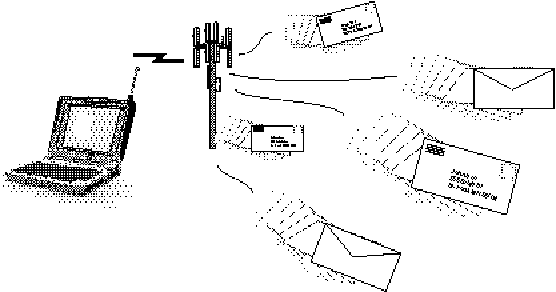
A useful analogy for a CDPD connectionless network is the U.S. Postal Service. A letter is like a datagram. With a letter, there is information on the envelope that contains the destination address. When the sender drops a letter in a mailbox, he or she does not know the route the letter will take to reach its destination. Letters to the same address may not take the same route twice, just as datagrams may take different routes. All that matters to the sender is that the letters arrive at their destination.
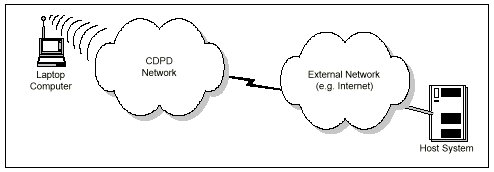
CDPD differs from circuit-switched in connection and data transmission. With circuit-switched data services a modem-to-modem connection is established and all data are transmitted in one continuous session or pipeline; the session is maintained until it is terminated. In CDPD no single end-to-end connection is established. Sessions, such as Telnet, are established at a logical level. The system routes datagrams from one network to another independent of the path. For CDPD to route the data packets to the appropriate network, a network to network communications link must be established. This can be accomplished with a device such as a router.
CDPD supports two connectionless network protocols, the Internet Protocol (IP) and the Connectionless Network Protocol (CLNP). These protocols allow for communication independent of any particular network hardware. CDPD is ideal for applications that use short bursts of data or small transactions such as electronic messaging, dispatching, credit authorizations, vehicle location tracking, etc.
| Send comments to webmaster Copyright © 1997 Derek Mc Donnell. All Rights Reserved. Last updated 07-Apr-1998. |
 |