|
Cellular Digital Packet Data Architecture and Data Capabilities |
CDPD operates by taking advantage of unused capacity in the AMPS analog cellular network. CDPD uses the idle time on the radio channel by interleaving voice calls with data packets. Even a busy cell in a cellular network has sufficient capacity for a full-duplex data channel (or channel stream) operating at a raw bit rate of 19.2 kbps.
As illustrated in Figure 1, mobile users access the CDPD network using a laptop computer or other computing device equipped with a wireless modem. The modem transmits on radio frequency channels that are shared with cellular voice transmissions. The data is received by a Mobile Data Base Station (MDBS), which manages data transmissions on cellular channels at its cell site. The MDBS delivers the data to the core of the CDPD network, the Mobile Data Intermediate System (MD-IS). The MD-IS routes data to off-the-shelf routers in the CDPD network and other interconnecting networks for delivery to the final destination host system.
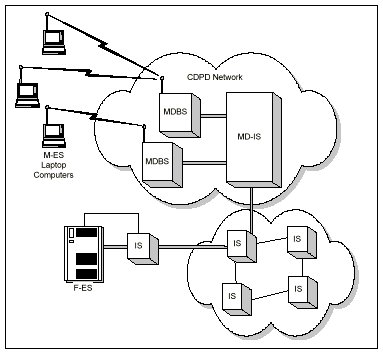
CDPD uses industry-standard networking protocols. By routing IP datagrams (Network Layer packets), CDPD facilitates connection to existing corporate and public data networks. The intermediate server (IS) shown in Figure 1 is an IP router resident within the CDPD service providerís network.
| Send comments to webmaster Copyright © 1997 Derek Mc Donnell. All Rights Reserved. Last updated 07-Apr-1998. |
 |