|
|
Q: What is Cellular Circuit-Switched Data? |
The circuit-switched cellular network is the most widespread option available today to transmit data.
It uses the current analog voice cellular circuits, referred to as the Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS), to transmit data between a mobile terminal, such as a laptop computer, and another computer system.
The term "circuit-switched" refers to the establishment of a dedicated connection or "circuit" between two end points (modem-to-modem). Because the connection remains fixed for the duration of the call, data over circuit-switched is often referred to as a "connection-oriented" transmission. See Diagram in below for an example of how cellular circuit-switched data works.
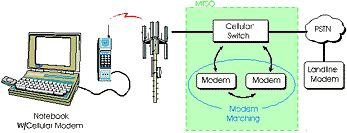
The current circuit-switched network features these characteristics for data:
Circuit-Switched data is most cost-effective for applications requiring large data file transfers, such as faxing, E-Mails with attachments, and image or graphic files.
Lotus' cc:Mail Mobile™ is an example of an efficient circuit-switched application that is designed for short sessions. A cc:Mail Mobile user can retrieve and send electronic mail in a batch mode that minimizes time on the cellular network.
| Send comments to webmaster Copyright © 1997 Derek Mc Donnell. All Rights Reserved. Last updated 07-Apr-1998. |
 |