|
Metricom |
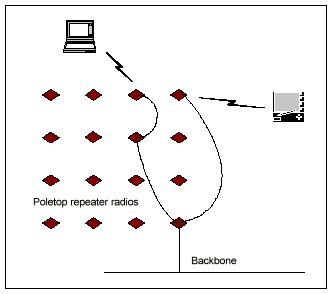
Metricomís network, Ricochet, differs from other wireless data networks by making use of the unlicensed band from 902 to 928 MHz. Mobiles communicate with small base stations (repeaters) that are attached to light poles. Ricochet has been designed as a campus or metropolitan-area solution.
Metricomís Ricochet primary application is to give user's access to the Internet. By offering modem gateways, it is also suited for applications that currently use landline modems.
Since Metricom uses unlicensed bands, users have secondary status. If a mobile unitís communications interfere with a primary userís communications, the mobile user must stop using the band. There are a large number of licensed (primary) users of the band. Additionally, secondary users must accept interference from licensed users. For this reason, users should think twice before using Ricochet for mission-critical applications.
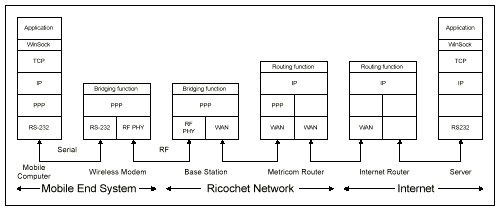
Ricochet provides data rates from 4.8 kbps BPS to 28.8 kbps. Mobile computers connect to wireless modems using an RS-232 serial connection. The wireless modem communicates with base stations using a packet protocol. Base stations relay messages to the backbone network if it is within range or relay messages via other base stations to the backbone. Base stations communicate between each other at a higher rate of 100 kbps. Routing decisions are made by the base stations based on latitude and longitude information. Metricomís internal network is completely proprietary and no additional details are available.
Metricom only has limited support for mobility. Wireless modems cannot be operated while moving at more than six miles per hour.
Metricom has deployed Ricochet in the San Francisco Bay Area, Seattle and Washington DC. More cities are scheduled for the future. For good performance, Metricom must deploy a high density of base stations. Even though the base stations are relatively inexpensive, one estimate projects that 100,000 base stations would be needed just to provide nationwide.
Metricom will most likely evolve into a campus or metropolitan solution. It is quite unlikely that its coverage could ever come close to the coverage of other networks such as CDPD.
Ricochet's basic service is to provide access to the Internet, where PPP is used between the mobile system and a router in the Metricom network for carrying TCP/IP traffic. Ricochet also provides a service called Telephone Modem Access (TMA) where the network simulates a modem connection. Such connections support any protocol designed for modem communications so long as the protocol can withstand higher delays than traditional modem connections.
| Send comments to webmaster Copyright © 1997 Derek Mc Donnell. All Rights Reserved. Last updated 07-Apr-1998. |
 |