|
Fast-Packet Switching |
Fast-Packet Switching
Teledesic's space-based network uses fast-packet switching. Communications are treated within the network as streams of short, fixed-length packets. Each packet contains a header that includes destination address and sequence information, an error-control section used to verify the integrity of the header, and a payload section that carries the digitally-encoded user data (voice, video, data, etc.). Conversion to and from the packet format takes place in the terminals at the edge of the network.
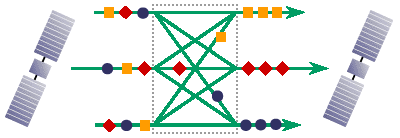
The topology of a LEO-based network is dynamic. The network must continually adapt to these changing conditions to achieve the optimal (least-delay) connections between terminals. The Teledesic Network uses a combination of destination-based packet addressing and a distributed, adaptive packet routing algorithm to achieve low delay and low delay variability across the network. Each packet carries the network address of the destination terminal, and each node independently selects the least-delay route to that
destination. Packets of the same session may follow different paths through the network. (See Figure 2.) The terminal at the destination buffers and if necessary reorders the received packets to eliminate the effect of timing variations.
| Send comments to webmaster Copyright © 1997 Derek Mc Donnell. All Rights Reserved. Last updated 07-Apr-1998. |
 |